Anatomical Engineering
Developing bio-inspired robotic systems and assistive devices through biomechanical analysis, EMG-controlled interfaces, and anatomical modeling.
Ankle exoskeleton with series elastic actuation to assist age-related plantarflexor muscle weakness
Interactive 3D Model
Click and drag to rotate, scroll to zoom, right-click to pan
Technical Design Rendering
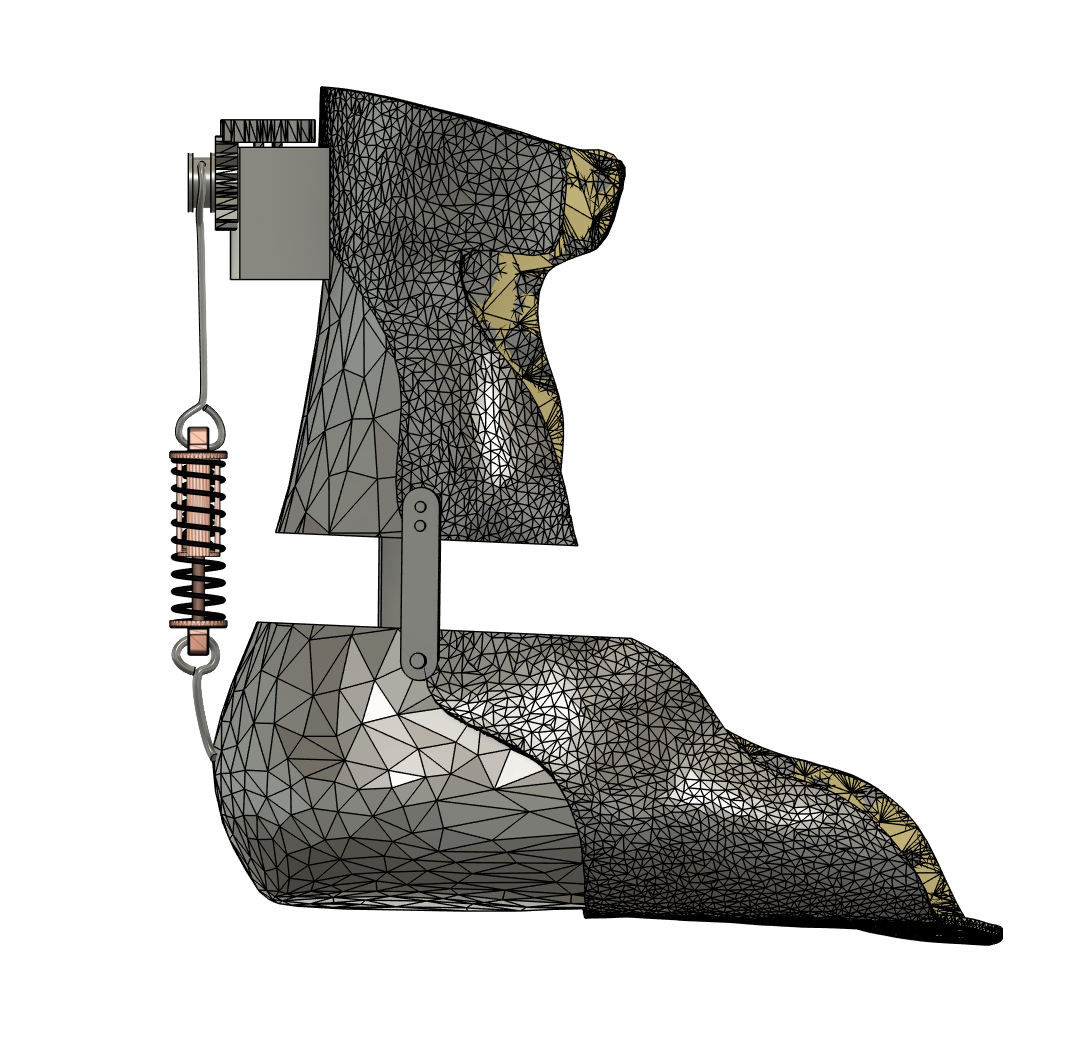
Side view showing series elastic actuation system
Project Overview
Age-related plantarflexor weakness affects over 61 million adults, reducing ankle power during push-off and increasing fall risk. Using OpenSim biomechanical modeling, we designed a series elastic actuator ankle exoskeleton that delivers optimally-timed assistive torque during late stance.
The device reduced metabolic cost from 575 J to 553 J (96% restoration), provided up to 100 Nm plantarflexion moment during push-off, and achieved 90% motor efficiency with a total system mass of just 1.87 kg.
Key Technical Specifications
Actuation System
- • Maxon EC-4pole 30 motor (200W, 90% efficiency)
- • GP 32 HP planetary gearhead (53:1 ratio)
- • Custom spring (k = 3175 N/m, stores 31.5 J)
- • Bowden cable transmission (3.78 cm pulley)
Performance
- • 36.2 W continuous power, 89.7 W peak
- • Up to 100 Nm plantarflexion torque
- • 96% metabolic efficiency restoration
- • Total system mass: 1.87 kg
Continuous proportional control system using analog muscle activation signals
Control System Demo
Analog EMG Control in Action
Proportional Response
Precise Movement Control
Project Overview
Analog EMG Control System
This advanced system uses analog electromyography (EMG) sensors to detect continuous muscle activation levels, enabling proportional control of the tentacle's four degrees of freedom. Unlike binary systems, this provides smooth, natural movement that responds to the intensity of muscle contractions.
Research Application
This project was developed for research studies investigating referential control of agonist-antagonist muscle pairs. The system explores how humans can intuitively control robotic devices through natural muscle activation patterns, advancing our understanding of human-machine interfaces for prosthetics and assistive devices.
Binary bioelectric control system using muscle activation signals
Project Documentation
Binary EMG Controlled Tentacle Demonstration
Project Overview
EMG Control System
This system uses electromyography (EMG) sensors to detect muscle contractions, converting biological signals into digital control commands for the tentacle.
Binary Control Logic
The system operates on binary muscle activation patterns, where specific muscle contractions trigger predetermined tentacle movements, creating an intuitive brain-to-machine interface.
Applications
Assistive Devices
Assistive technology for individuals with mobility limitations.
Prosthetics
Advanced prosthetic control systems using natural muscle activation patterns.
Rehabilitation
Rehabilitation tools for motor function recovery and therapy applications.
Interactive control system with real-time joystick input for precise tentacle manipulation
Interactive 3D Model
Click and drag to rotate, scroll to zoom, right-click to pan
Project Documentation
Analog Joystick Controlled Tentacle Demonstration
Control System
Hardware Components
- • Custom 3D-printed base and vertebrae
- • Counterwound cable backbone system
- • Four outer control cables
- • Two servo motors for actuation
- • Arduino Leonardo microcontroller
Control Features
- • Analog joystick interface
- • Real-time directional control
- • Opposing cable pair actuation
- • Smooth, continuous movement
- • Intuitive user interaction
Tentacle mechanism with counter pulling capabilities
Click and drag to rotate, scroll to zoom
Project Documentation
2 Degree of Freedom Tentacle Demonstration
Technical Features
Actuation System
- • Spring steel backbone for structural support
- • Steel cable actuation system
- • Central coiled spring for passive resistance
- • Strategic cable pulley placement
Design Features
- • Custom 3D-printed base component
- • Set screw securing mechanism
- • Curved cable path optimization
- • Rotation prevention system
Bio-inspired single degree of freedom finger mechanism with cable-driven actuation
Interactive 3D Model
Click and drag to rotate, scroll to zoom, right-click to pan
Key Features
- • Heat-formed nylon tubing for structural integrity
- • Precision-cut notches for controlled flexion
- • Braided Kevlar actuation cable for durability
- • Ergonomic key ring base for user comfort
- • Scalable design for full hand implementation
Project Documentation
Test Finger
Replication
Full Hand Demonstration

